There seems to be a constant focus in the media on terpenes and cannabinoids when it comes to marijuana, but is that all there is to this endlessly surprising plant? The popularity of marijuana has surged both scientifically and publicly, and the focus has shifted to the most distinctive and popular compounds. Several lesser-known compounds within marijuana could have a drastic effect on neurological metabolic health, including flavonoids, stilbenes, and lignans, as well as alkaloids, cinnamic acid, and saponins. “The entourage effect” refers to the synergistic effects of these compounds on phytocannabinoids throughout the plant, from the seeds and roots to the flower buds (Bautista et al., 2021). The entourage effect continues to be researched, but the less well-known components of marijuana are crucial in developing therapeutics and gaining a better understanding of consumer benefits.
Phenolic compounds in cannabis: what are they?
Phenolic compounds are one of the largest groups of secondary metabolites produced by plants. “These compounds represent more than 10,000 different structures, including phenolic acids, such benzoic and hydroxycinnamic acids, flavonoids such as flavonols and flavones, stilbenes and lignans,” (Andre et al., 2010). Many of these compounds work together with the natural metabolic and neurological pathways that exist in the body. Recently, a group of phenolic compounds called flavonoids increased in popularity in the scientific community.
What are flavonoids in cannabis?

Figure 4.20a – Cannflavin Molecule
Flavonoids can be found in everyday products, such as fruits, vegetables, flowers, tea, oil, and milk. The medicinal properties of flavonoids such as cannflavin are becoming more widely recognized due to their potential therapeutic benefits. Recent studies have shown that cannflavin has antioxidative and anti-inflammatory properties like other flavonoids. (Bautista et al., 2021). While cannflavin is specific to cannabis (Figure 4.20a), consumers interact with flavonoids daily. Scientific exploration into the different compounds found in marijuana continues to reveal anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidizing properties as a common theme, further confirming the credibility of their synergistic effects.
Lignans in Cannabis: what are they?
Lignans are phenolic compounds found in numerous plant species, including marijuana, and have been widely studied for their therapeutic properties. “Traditionally, health benefits attributed to lignans have included a lowered risk of heart disease, menopausal symptoms, osteoporosis, and breast cancer,” (Rodríguez-García, C., et al., 2019). Lignans are primarily found in the seeds of plants and are currently being produced and consumed as a daily supplement from flaxseed oil. Lignan precursors have been shown to convert into natural estrogenic compounds once ingested by bacteria in the stomach, which are then naturally processed by the body (Rodríguez-García, C., et al., 2019). The legalization of marijuana has revealed new insights into the potential of lignans in today’s pharmaceutical market, which is typically studied as a dietary supplement for women’s overall health.
Can cannabis antioxidants be beneficial to your health?
Society’s awareness of physical health is on the rise, which has led to an increase in interest in antioxidants as well as the fight against natural aging. A compound known as an antioxidant helps protect cells, and the human body, from natural oxidation caused by time and environmental factors. The effects of oxidative stress and inflammation are key to the development of many diseases, such as diabetes, age-related macular degeneration, and Alzheimer’s disease (Reinisalo, M., et al., 2015). As cells age, their capacity to produce antioxidants diminishes, decreasing the ability of the cell to respond to damage and repair itself. It’s been demonstrated that stilbene compounds, a diverse group of natural defense phenolics found in grapes, berries, and conifer bark waste, have protective effects against aging-related diseases” (Reinisalo, M., et al., 2015).
Can cannabis stilbenes be beneficial for health?
As a chemopreventive compound, stilbenes actively interfere with tumor growth and generation, target inflammation, and help cell cycle receptors, making them more likely to be used as anticarcinogens (Sirerol, J. A., et al., 2016). Using the natural cell generation process, stilbenes prevent inflammation, oxidative stress, and cancer cell reproduction. Figure 4.20b shows many of the different metabolic and neural pathways affected by this compound (2020). Manufacturers produce stilbene compounds from grape leaves and stem bi-products through chemical extraction. The medicinal properties of this plant have been known for hundreds of years, though specific chemical interactions have only been discovered recently.
What is Cinnamide in cannabis?
The use of cinnamic acids produced by boiling cannabis roots for treating illnesses dates back to the early 1500s. Cinnamide, one of the compounds present in boiled solution, exhibits anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, and analgesic properties, and may help with gout and joint pain (Ryz, N. R., et al., 2017). The results documented the therapeutic benefits of boiling cannabis roots in a wide range of ailments, even though doctors in the 16th century were unaware of these interactions. This is seen in Figure 4.20c. As a result, consumers have a simpler experience today. These extracts hold the potential for creating a daily capsule that could prevent many arthritic debilitations later in life. The prevention of diseases, anti-aging, and delaying the onset of death is always at the forefront of scientific research.
 Saponin in Cannabis: what is that?
Saponin in Cannabis: what is that?
A saponin compound, however, may provide a stronger weapon in the fight against obesity, a pressing health problem today. The obesity epidemic has become a growing concern as grocery prices rise daily and household budgets become tight. Saponin compounds have the potential to prevent cardiovascular disease and Type II diabetes. Derived from hemp seed oil, saponin can play a large part in reducing the fat storage of the body and helping the pancreas digest fat (Marrelli, M., et al., 2016). Effects of Saponins on Lipid Metabolism determined two possible effects:
- a safer weight management control drug without the severe adverse side effects in the pharmaceutical market
- a potential preventative or treatment for diabetic ailments.
As a result, saponin restored the insulin response function in the body, causing an increase in insulin production from the pancreas. Saponins actively inhibit pancreatic lipase and decrease fat absorption after digestion (Marrelli, M., et al., 2016). This study may debunk the socially popular munchie’s side effects! Even though there are many compounds present in marijuana that are unknown to the general public, there are some that are well known to the scientific as well as the social communities.
What are Alkaloids?
Alkaloids have a deep history in the medical field, their importance and versatility transcend cultures. There are recordings in Traditional Chinese Medicine of the use of alkaloids for a plethora of ailments and it is considered one of the most important ingredients required in the practice. Through their interaction with both metabolic and neural pathways within the body, they help inhibit tumor growth, boost anti-inflammatory receptor responses, and act as both sedatives and antipsychotics. Natural alkaloids: basic aspects, biological roles, and future perspectives describe several neurological implications for future pharmaceuticals primarily through inhibiting certain receptors in the body by regulating inner homeostasis in cell cycles and inducing pro-inflammatory cell production (2014). Other, more well-known, alkaloids include cocaine, caffeine, and nicotine. The popularity of these compounds speaks to the effectiveness alkaloids have on the metabolic and neurological systems. Cannabis is not an alkaloid, but it has been demonstrated to contain spermidine-type alkaloids as well as Annhydrocannabisativine alkaloids (Mechoulam, R. 1989). As marijuana’s popularity rises, continuous research is being conducted to further understand the role these specific alkaloids play.

Papaveraceae – a plant rich in alkaloids
Marijuana has a rich medical history that dates back centuries. It is becoming increasingly important in pharmaceutical research to understand the specifics of these compounds and their interactions. Cannabis contains a wide variety of compounds, including cannabinoids, terpenes, and lesser-known compounds, all present from the seeds to the buds produced at the end of the flowering process. As we continue to learn more about flavonoids, stilbenes, and lignans, as well as alkaloids, cinnamides, and saponins, their individual and synergistic properties will continue to be explored and studied. With health benefits such as anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and diabetic resistance, it is easy to understand why more and more individuals are taking an interest in marijuana.
Works Cited
Andre, C., Larondelle, Y., & Evers, D. (2010). Dietary Antioxidants and Oxidative Stress from a Human and Plant Perspective: A Review. Current Nutrition & Food Science, 6(1), 2–12. https://doi.org/10.2174/157340110790909563
Bautista, J. L., Yu, S., & Tian, L. (2021). Flavonoids in Cannabis sativa: Biosynthesis, Bioactivities, and Biotechnology. ACS Omega, 6(8), 5119–5123. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c00318
Ryz, N. R., Remillard, D. J., & Russo, E. B. (2017). Cannabis Roots: A Traditional Therapy with Future Potential for Treating Inflammation and Pain. Cannabis and Cannabinoid Research, 2(1), 210–216. https://doi.org/10.1089/can.2017.0028
Rodríguez-García, C., Sánchez-Quesada, C., Toledo, E., Delgado-Rodríguez, M., & Gaforio, J. (2019). Naturally Lignan-Rich Foods: A Dietary Tool for Health Promotion? Molecules, 24(5), 917. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24050917
Reinisalo, M., Kårlund, A., Koskela, A., Kaarniranta, K., & Karjalainen, R. O. (2015). Polyphenol Stilbenes: Molecular Mechanisms of Defence against Oxidative Stress and Aging-Related Diseases. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2015, 1–24. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/340520
Sirerol, J. A., Rodríguez, M. L., Mena, S., Asensi, M. A., Estrela, J. M., & Ortega, A. L. (2016). Role of Natural Stilbenes in the Prevention of Cancer. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2016, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/3128951
Marrelli, M., Conforti, F., Araniti, F., & Statti, G. (2016). Effects of Saponins on Lipid Metabolism: A Review of Potential Health Benefits in the Treatment of Obesity. Molecules, 21(10), 1404. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21101404
Mechoulam, R. (1989, January 1). Chapter 2 Alkaloids in Cannabis Sativa L. (A. Brossi, Ed.). ScienceDirect; Academic Press. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0099959808602278#:~:
text=Annhydrocannabisativine%20is%20another%20alkaloid%20found
Pecyna, P., Wargula, J., Murias, M., & Kucinska, M. (2020). [Figure 1] Biomolecules, 10(8), 1111. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10081111



 Modern Canna
Modern Canna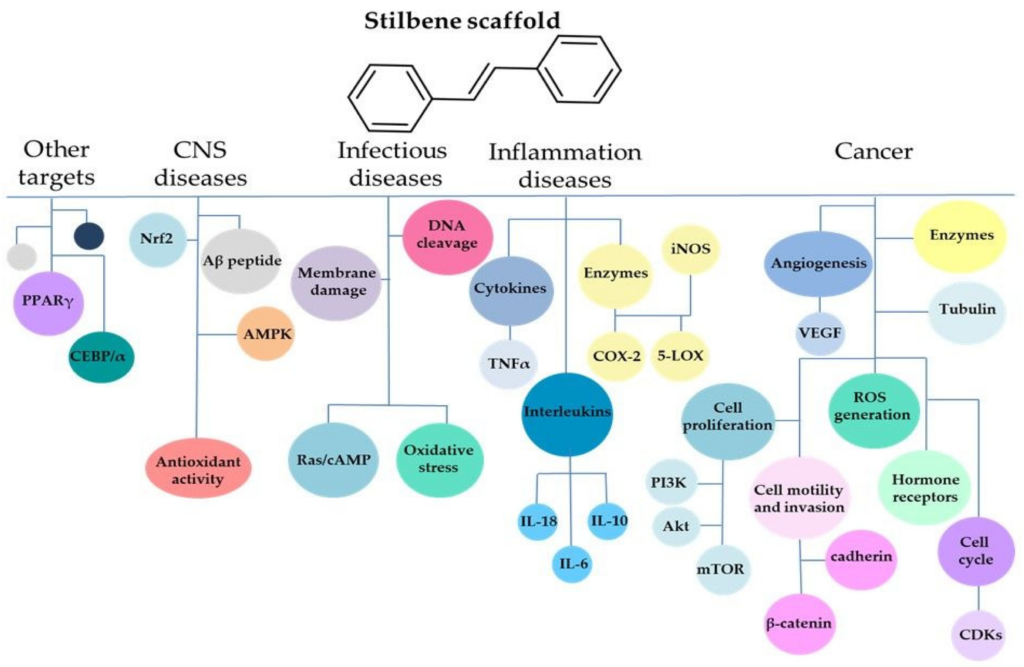
 Saponin in Cannabis: what is that?
Saponin in Cannabis: what is that?